Chapter 20 : Poverty, Inequality and Unemployment | Short Questions [2 Marks each]
1. What do you mean by poverty?
Answer: Poverty is the inability to fulfill the minimum requirements of life.
2. What is poverty line? [2019]
Or, Define poverty line. [2017]
Answer: Poverty line refers to the money value of the minimum quantities of those goods and services which are needed for the subsistence of an individual.
3. What is poverty gap?
Answer:

4. Mention two reasons for the persistence of poverty in India.
Or, Mention two causes of poverty in India. [2015]
Answer: Two reasons for the persistence of poverty in India are-
(i) Unemployment and low wages and
(ii) Income inequality.
5. Mention two measures adopted for the eradication of poverty in India.
Or, Mention any two measures adopted for the removal of poverty in India. [2018]
Answer: Following measures can be adopted for the removal of poverty in India:
(a) Jawahar Rozgar Yojana (JRY)
(b) Prime Minister’s Rozgar Yojana (PMRY)
6. What is head count ratio for measurement of poverty? [2022]
Answer: Under head count ratio method for measurement of poverty, the number below the poverty line is estimated and this number is expressed as a percentage of total population.
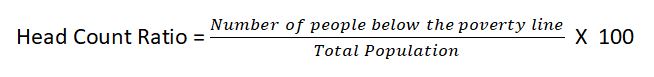
7. For what purpose was the Mahalanobis Committee (1960) set up?
Answer: The Mahalanobis Committee was set up in 1960 to study the problem of inequality in the distribution of income.
8. What is the objective behind enactment of ceiling on land holdings?
Answer: In order to remove inequality in the distribution of land ownership in West Bengal, Land ceiling laws have been enacted.
9. What can we know from Madalgi’s study on inequality of income in India?
Answer: From Madalgi’s study on inequality of income in India we know that the inequallity is stronger in urban areas than in rural areas.
10. Mention two causes of inequality in the distribution of income.
Or, Mention two causes of income inequality in India. [2016, 2018]
Answer: Two causes of income inequality in India are –
(i) Inheritance law and (ii) Tax evasion.
11. Mention two measures adopted for reducing inequality in the distribution of income in India.
Answer: Following measures can be adopted for reducing inequality in the distribution of income in India:
(a) the payment of bonus has been made compulsory in each industry.
(b) a ceiling on land holdings has been imposed on households in rural areas. The government takes over the surplus land and redistributes them among rural landless labourers.
12. What is private concentration?
Answer: Private concentration refers to a few industrial firms controlling the lion’s share of output. Such concentration is based on the ownership of the industrial units.
13. What is monopoly firm? Give examples.
Answer: Sometimes it is found that in a particular industry the total output is dominated by a few large firms. These large firms are known as monopoly firms.
14. What is monopoly house? Give examples.
Answer: When a few large firms dominate the production of a number of important commodities so that in effect they control the entire private sector of the economy. Such a group of firms is called a monopoly house.
15. Distinguish between monopoly firm and monopoly house.
Answer:
| Monopoly firm | Monopoly house |
|---|---|
| Sometimes it is found that in a particular industry the total output is dominated by a few large firms. These large firms are known as monopoly firms. | When a few large firms dominate the production of a number of important commodities so that in effect they control the entire private sector of the economy. Such a group of firms is called a monopoly house. |
16. What is seasonal unemployment? [2015]
Answer: When workers remain unemployed in some seasons of the year, it is called seasonal unemployment. For example: In a lean season, there exists seasonal unemployment in agriculture.
17. What is disguised unemployment? [2016, 2022]
Answer: Disguised unemployment refers to those surplus workers who are apparently involved in any work but are not contributing to total output. Therefore, their contribution to total product is zero.
18. What is structural unemployment?
Answer: Structural unemployment is unemployment that occurs due to structural changes in the economy. Structural unemployment takes place in the case of changes in technology or changes in the pattern of demand.
19. What do you mean by technological unemployment? [2017]
Answer: Technological unemployment is unemployment that occurs due to the introduction of new technology. For example: when a new technology is introduced, old technicians lose their jobs.
20. Recommend two measures for solving the problem of rural unemployment in India.
Answer: To solve the problem of rural employment in India, the following measures may be adopted by the government of India:
(a) Agro-based industries should be developed in rural areas.
(b) Minor irrigation facilities should be expanded.
21. State two measures of increasing unemployment in industrial and urban areas of India.
Answer: To solve the problem of unemployment in industrial and urban areas in India following measures may be adopted by the government of India:
(a) Small and cottage industries should be expanded.
(b) Technical and vocational education are to be expanded.
22. What are the measures that can be adopted to solve the unemployment problem among the educated youth?
Answer: Following measures can be adopted to solve the unemployment problem among the educated youth:
(a) Training for Rural Youth for Self-Employment (TRYSEM)
(b) Self-Employment for the Educated Urban Youth (SEEUY)
23. What is the objective of Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Scheme (MGNREGS)? [2019]
Answer: The objective of Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Scheme (MGNREGS) is to provide employment of 100 days per year to one able member of a rural family.
Like our post?
We are available with lots and lots of commerce-related content.





[…] Unemployment (MCQ) দারিদ্র্য, বৈষম্য ও বেকারি (MCQ) Poverty, Inequality and Unemployment (SAQ) দারিদ্র্য, বৈষম্য ও বেকারি (SAQ) Poverty, Inequality […]